Flink流处理API
Environment
对于Bounded有界流数据,可以采用ExecutionEnvironment创建执行环境;对于Unbounded无界流数据,可以采用StreamExecutionEnvironment创建。具体创建方法如下:
StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironment(parralism);
StreamExecutionEnvironment.createRemoteEnvironment(hostname,port,jars);
StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); // 自动识别当前执行环境并实例化执行环境对象【推荐】
Source
从集合中读取数据
DataStream<Tuple2> input = env.fromCollection(Arrays.asList(
new Tuple2(1, "hello"),
new Tuple2(2, "world"),
new Tuple2(3, "hello"),
new Tuple2(4, "flink")
));
DataStream<Tuple2> input = env.fromElements(
new Tuple2(1, "hello"),
new Tuple2(2, "world"),
new Tuple2(3, "hello"),
new Tuple2(4, "flink")
);
从文件读取数据
env.readFile(new FileInputFormat<Object>() {
@Override
public boolean reachedEnd() throws IOException { return false; }
@Override
public Object nextRecord(Object reuse) throws IOException { return null; }
},FILE_PATH);
env.readTextFile(FILE_PATH, CHAR_SET)
从Kafka读取数据
- 引入flink-connector-kafka组件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-kafka_${scala.version}</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
- 从Kafka消费数据
Properties properties = new Properties() ;
FlinkKafkaConsumer<ObjectNode> kafkaConsumer = new FlinkKafkaConsumer<>(
"kafkaTopic",
new JSONKeyValueDeserializationSchema(false), //要求Kafka中的数据已经序列化为比特数组
properties
);
kafkaConsumer.setStartFromEarliest(); // 尽可能从最早的记录开始
kafkaConsumer.setStartFromLatest(); // 从最新的记录开始
kafkaConsumer.setStartFromTimestamp(1000); // 从指定的时间开始(毫秒)
kafkaConsumer.setStartFromGroupOffsets(); // 默认的方法
DataStream<ObjectNode> inputSource = env.addSource(kafkaConsumer);
Flink消费Kafka时支持分区偏移量、checkpoint容错、分区发现、时间戳抽取以及watermark 发送**,此处参考官方文档。
自定义Source源
public static class WordCountSource implements SourceFunction<String> {
public boolean flag = false;
@Override
public void run(SourceContext<String> ctx) throws Exception {
List<String> sourceTemplate = new ArrayList<>() ;
while (!flag) {
for (String word : sourceTemplate) {
ctx.collect(word);
}
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
this.flag = true;
}
}
Transform
| Transform Type | Function Meaning | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| MapFunction | [□□□] → map → [●●●] | 将数据一对一转换 |
| FlatMapFunction | [□] → flatMap → [●●●] | 将数据一对多转换 |
| FilterFunction | [□□□] → filter → [□□] | 将数据进行过滤 |
| KeyBy | [□□□] → keyBy → [{□},{□□}] | 将数据进行分类并重分区 (DataStream → KeyedStream) |
| Rolling Aggregation | [{□},{□□}] → sum|min|max|minBy|maxBy → [{□},{□}] | 将分组后的数据进行滚动聚合 (KeyedStream → DataStream) |
| ReduceFunction | [{□},{□□}] → reduce → [{●},{●}] | 将分组后的数据进行规约 (KeyedStream → DataStream) |
| Split&Select (OutputSelector) | [□□□] → split&select → [□,□□] | 将数据流拆分成多个组,可以理解为给数据流盖戳 (DataStream → SplitedStream) |
| Connect&CoMap | [□,●●] → connect&coMap → [□●●] | 将2个数据流合并到一个数据流 (DataStreams → ConnectedStream) |
| Union | [□,□,□□] → union → [□□□□] | 将多条数据类型相同的数据流合并成一条流 (DataStreams → DataStream) |
补各种DataStream转换图
时间语义
Flink 时间语义指的是处理数据时,对数据时间戳进行归类:
- ProcessingTime: 处理时间,指的是数据被处理的时间;
- EventTime: 事件时间,指的是数据产生时自带的时间;
- IngestionTime: 摄入时间,指的是数据读入到Flink的时间。
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime);
Watermark水位线
当采用EventTime事件时间时,数据到来的事件时间可能是乱序的,为了处理此问题引出Watermark概念。例如,某学校大部分学生能在9:05分前到,而班车发车时间是9:00,因此为了能够使大部分同学上车,就将司机手表时间调慢5分钟。
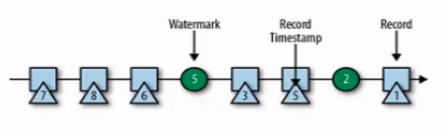
Watermark具有如下特点:
- Watermark是一条特殊的数据记录;
- Watermark必须单调递增,以保证事件时间的时钟向前推进,而不是时间倒退;
- Watermark与数据的时间戳相关。
Watermark本质也是一个StreamElement,它是数据流中的一个与数据时间戳相关的数据记录。当我们设置延迟时间和窗口时间都是3s时,对于上列的数据,其watermark的次序为:
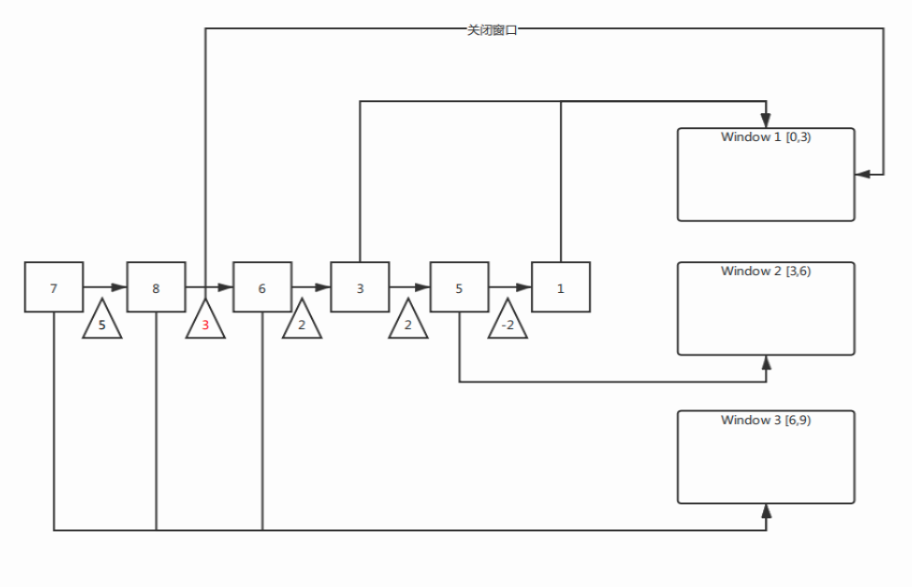
另外Watermark作为时间戳需要同时通知下游任务,因此从上游角度来说,Watermark需要广播给下游;而从下游角度来看,当接收到不同上游的不同Watermark,其保证的是上游Watermark时间戳的任务已经完成,因此对于下游来说它应该取最小的Watermark,象征最小的Watermark之前的任务已经处理完成。
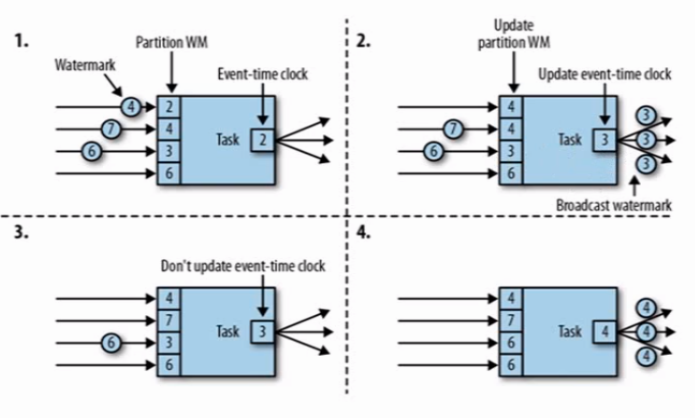
flink主要提供了两种Watermark,即:
- forMonotonousTimestamps (AscendingTimestampsWatermarks)
- forBoundedOutOfOrderness (BoundedOutOfOrdernessWatermarks)
在Java中使用的方法是:
DataStream<Salary> salaryStream = env.addSource(new SalarySource())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy
.<Salary>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofDays(30 * 48)) //指定Watermark的生成方式
.withTimestampAssigner((event, assigner) -> event.getPayday()) // 指定事件时间EventTime的生成方式
);
状态控制
Flink提供自动的状态管理,其中主要包括:
- 算子状态(Operator State):算子状态针对整个算子方法,各个算子任务独有一个状态
- CheckpointFunction
- 键值状态(Keyed State):键值状态针对的是一个键的状态,一个算子有多个Hash键,每个键有一个键值状态
- ValueState
- MapState<UK,UV>
- ListState
- ReduceState
- AggregatingState<IN,OUT>
- ValueState
ValueState<RestrictedMap> rmap;
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
this.rmap = this.getRuntimeContext().getState(
new ValueStateDescriptor<>("rmap", RestrictedMap.class)
);
}
public class OperatorStateTest
extends KeyedProcessFunction<K, IN, OUT> implements CheckpointedFunction {
@Override
public void snapshotState(FunctionSnapshotContext context) throws Exception {}
@Override
public void initializeState(FunctionInitializationContext context) throws Exception {}
状态后端
Flink的状态后端主要分为,具体的介绍详见官方文档:
- Memory: 状态保存到TaskManager的JVM内存中;
- FsStateBackend: 将checkpoint保存到文件系统中,例如HDFS;对于本地状态依然保存在内存中;
- RocksDBStateBackend: 将所有状态序列化,保存到本地的RocksDB中存储。
Sink
Kafka Sink
- 引入flink-connector-kafka组件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-kafka_${scala.version}</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
- 向Kafka生产数据
Properties properties = new Properties() ;
FlinkKafkaConsumer<String> kafkaConsumer = new FlinkKafkaConsumer<>(
"demo-topic",
new SimpleStringSchema(),
properties
);
kafkaConsumer.setStartFromEarliest(); // 尽可能从最早的记录开始
kafkaConsumer.setStartFromLatest(); // 从最新的记录开始
kafkaConsumer.setStartFromTimestamp(1000); // 从指定的时间开始(毫秒)
kafkaConsumer.setStartFromGroupOffsets(); // 默认的方法
DataStream<String> streamSource = env.addSource(kafkaConsumer).shuffle();
streamSource.addSink(new FlinkKafkaProducer<String>(
properties.getProperty("bootstrap.servers"), //Kafka地址
"sink-test", //Kafka Topic名称
new SimpleStringSchema() //序列器
));
Window
- 时间窗口(Time Window)
- 滚动时间窗口(Tumbling Windows):时间对齐,窗口长度固定,没有重叠;
- 滑动时间窗口(Sliding Windows):窗口长度固定,可以有重叠,某个数据同时属于(window size / window slide);
- 会话窗口(Session Windows):一段时间(timeout)没有接受到数据就会产生新的会话窗口,时间不对齐。
- 计数窗口(Count Window)
Window API
窗口分配器window()方法应当在keyBy后使用:
// Note: This operation is inherently non-parallel since all elements have to pass through the same operator instance.
// 全部数据会汇总到一起做window开窗操作,相当于global()的分区,不推荐使用
inputSource.windowAll(
TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.minutes(1))
);
inputSource
.keyBy("id")
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.minutes(1))); // 滚动时间窗口,可直接使用.timeWindow(...)
inputSource
.keyBy("id")
.window(EventTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.minutes(1))); // 会话时间窗口
inputSource
.keyBy("id")
.countWindow(100); // 滚动计数窗口
inputSource
.keyBy("id")
.countWindow(100,50); // 滑动计数窗口
Window Function
Window Function定义了要对窗口收集的数据进行计算的操作(keyBy后的聚合操作),可以分为如下两类:
- 增量聚合函数(Incremental Aggregation Functions)
- 每条数据到来就计算,保持简单状态,如: ReduceFunction, AggregateFunction
- 全窗口函数(Full Window Function)
- 先把窗口内的数据收集起来(称为保存状态State),等到计算时在遍历窗口内的所有数据,如: ProcessWindowFunction, WindowFunction
// ReduceFunction
inputSource.keyBy("id")
.timeWindow(Time.minutes(5))
.reduce(new ReduceFunction<String>() {
@Override
public String reduce(String value1, String value2) throws Exception {
return null;
}
});
// AggregateFunction
inputSource.keyBy("id")
.timeWindow(Time.minutes(5))
.aggregate(new AggregateFunction<String, Integer, Integer>() { //AggregateFunction<IN, ACCUMLATOR, OUT>
@Override
public Integer createAccumulator() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Integer add(String value, Integer accumulator) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Integer getResult(Integer accumulator) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Integer merge(Integer a, Integer b) {
return null;
}
});
// WindowFunction
inputSource.keyBy("id")
.timeWindow(Time.minutes(5))
.apply(new WindowFunction<String, Integer, Tuple, TimeWindow>() { //WindowFunction<IN, OUT, KEY, W extends Window>
@Override
public void apply(
Tuple tuple,
TimeWindow window,
Iterable<String> input,
Collector<Integer> out) throws Exception {
Integer count = IteratorUtils.toList(input.iterator()).size();
out.collect(count);
}
});
其他API
trigger()触发器,定义了window什么时候关闭,触发计算并输出结果evitor()移除器,定义了移除某些数据的逻辑allowOutputLateness()允许处理迟到的数据sideOutputLateDate将迟到的数据放入旁路输出流getSideOutput()获取旁路输出流
